Deep Dive: Caldera
A deep dive into the Caldera building on one of the hottest themes of “rollups”, the modular blockchains, and a sneak peek into Caldera's ecosystem
This is a deep dive into Caldera and the overall Rollup ecosystem. It is meant to be a one-stop resource for you to gain a deep understanding and appreciation for Caldera. Along the way, you will also learn the importance of rollups in the blockchain space in general.
It is primarily written for a beginner-intermediate audience and only minimal prior familiarity is expected. I will attempt to build all understanding from the ground up.
So without further ado, let’s get started 🚀
According to its docs, Caldera is a rollup deployment platform that allows you to launch high-performance, customizable, application-specific rollups with the Arbitrum Nitro and Optimism Bedrock frameworks.
There are 3 key concepts that we need to know to get a thorough understanding of Caldera and its applications.
Rollups
Rollup Deployment platform or Rollup as a service (Raas)
Application-specific rollups
I’ll start with very simple explanations of each of these and go into much more detail further on in the essay.
Rollups
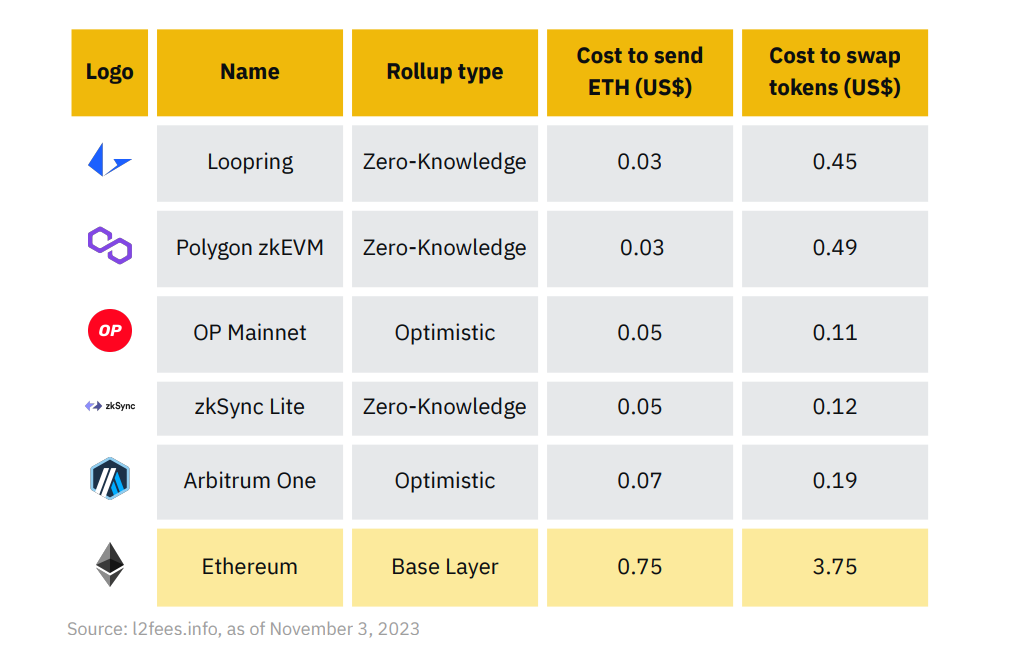
Ethereum is often criticized for being slow and costly, managing only 7-15 transactions per second compared to Visa's 100,000 per second. To make crypto more widely accepted and compete with traditional financial systems, it is crucial to increase transaction speed and reduce gas fees. A promising solution to enhance Ethereum's scalability is through the implementation of Rollups.
Rollups are a Layer 2 scaling solution for blockchains where a large group of transactions are combined into a single transaction, saving energy and space.
Let us understand this in more detail— on the Ethereum network, two main things can be posted on the blockchain: transactions and data. Transactions involve sending ETH from one address to another and data can be anything from simple messages to complex programs, known as smart contracts.
According to the Ethereum website, a rollup is a solution that executes transactions outside the main Ethereum chain but posts the final transaction data on the main chain. As Ethereum blocks have a limited capacity for data, let's say 100 transactions per block. When there are more than 100 transactions, Ethereum will select the top 100 based on the highest fees, leaving others to wait and making the network slow and unusable. But one of those 100 transactions can also be used to store data, instead of a normal transaction. And in that data, we can just write a whole bunch of other transactions. In a sense, if one data entry in the block could be 10 transactions, we have now effectively scaled to 1000 transactions per block by using the data portion instead of the transaction portion. This is how in general rollups work, rolling up a bunch of transactions and turning them into one piece of data to submit to the blockchain, instead of a bunch of singular entries—which saves a bunch of space.
There are two primary types of rollups:
Optimistic rollups: These assume all transactions are valid and submit batches without computation. However, there's a challenging period where transaction batch authenticity can be challenged.
Zk-rollups: These create cryptographic proofs to prove transaction validity, featuring a 'validity proof' for each transaction batch that must be submitted on the main chain.
Application-specific rollups
L2 solutions like rollups were developed in the first place to solve the scalability problems of L1 and have led to significant improvements in reducing average transaction fees and enhanced network throughput. This led to rollups being super cheap to transact with than the Ethereum L1.
But as L2s started to gain popularity, they started to suffer from the same issues as L1s, namely, scalability constraints. As each dApp is forced to compete with others for the same shared blockspace, fees started to rise. Even if they do not spike to the same level as Ethereum, the fluctuations can be enough for many users to start getting priced out, especially for transaction-heavy use cases such as gaming or SocialFi.
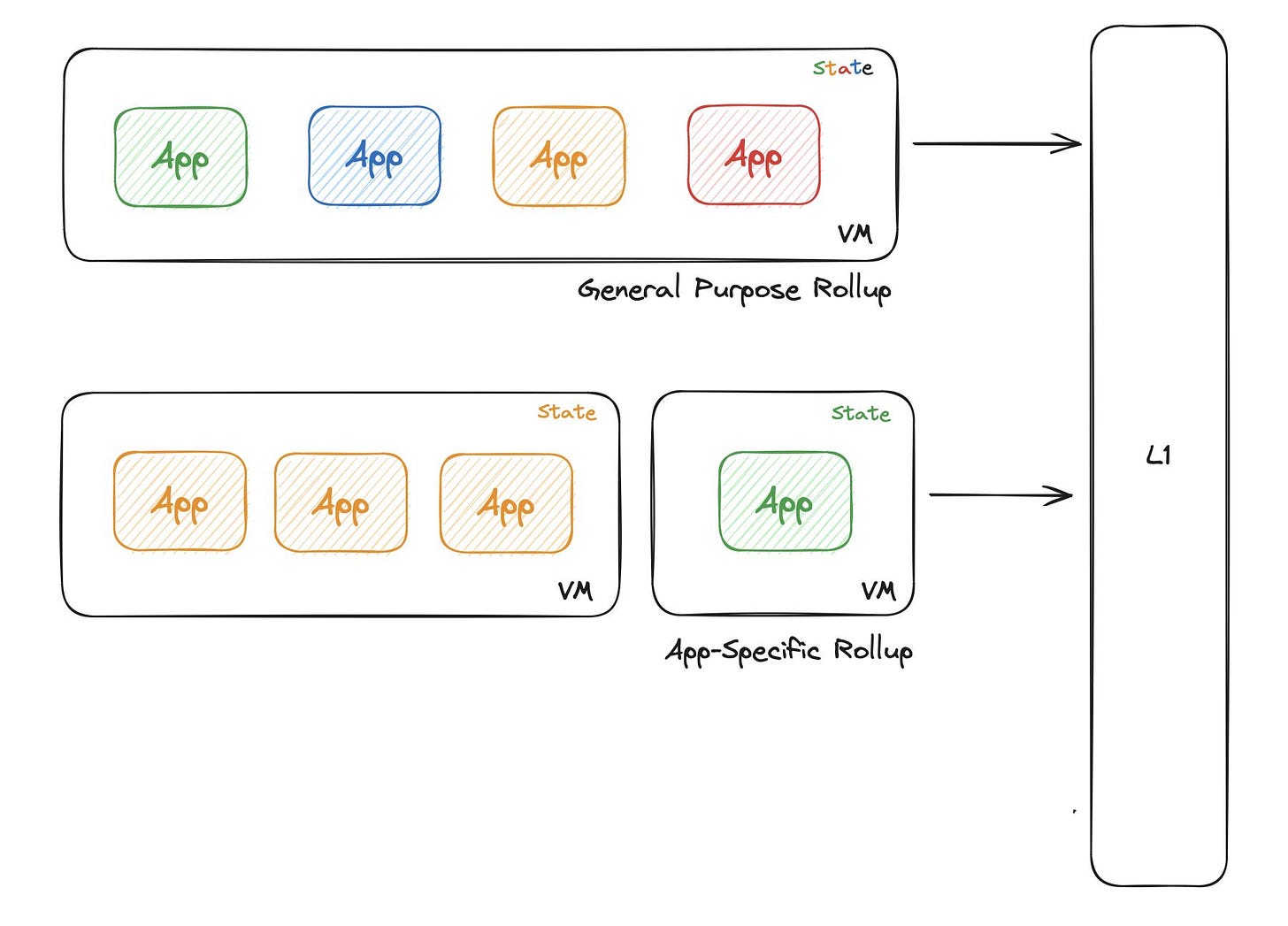
Additionally, deploying on a shared network like L1s or L2s limits the scope of customization as general-purpose L1s and L2s are designed to serve a wide variety of use cases, whereas some dApp developers might be looking for more optimized solutions. This led to the rise of customizable Appchains.
What are Appchains?
Appchains, or application-specific blockchains, are specialized chains designed for individual applications. An appchain ensures optimized performance and flexibility by eliminating the competition for computational and storage resources, which is common in public Layer 1 networks. This type of framework was popularized by the Cosmos ecosystem and has been followed by Polygon Superchains, Avalanche Subnets, and others.
2022 was the year many ‘popular’ dApps announced to move from a general-purpose chain to an app-specific chain, such as DeFi kingdoms, a popular game that saw $130 Million in daily volume and 400K daily transactions at peak, which decided to move from Harmony, a Layer 1, to have its own appchain on Avalanche subnet. Yuga Labs also intended to move from Ethereum when its highly anticipated NFT sale faced scalability issues. The appchain market saw its breakthrough when one of the biggest decentralized derivatives exchanges on Ethereum, dYdX announced that the next version would be built on its own appchain with its own set of validators using the Cosmos SDK.
The reason to move to one’s appchain is simple— customization. dYdX, being a trading platform, uses an orderbook model. To scale further, they needed more scalable systems, which wasn’t possible in their existing chain (Arbitrum) and required higher throughput, i.e., Transactions per Second (TPS). Hence they decided to have their own chain to maximize customizations while leveraging the composability and interoperability of Cosmos SDKs.
But appchains suffer from their own set of limitations and bottlenecks i.e. security. A vital part of the security of proof-of-stake blockchains is the chain’s number of stakers and validators. The more stakers a chain has, the more economic value they have in securing it. This makes it more difficult for an attacker to obtain a majority of the stake, making the chain more secure. The issue that Cosmos appchains run into is bootstrapping an initial set of validators. There are only a limited number of stakers and validators out there. Each app-chain can’t have a robust set of validators, especially as more and more app-chains get spun up. The result is that many appchains have very weak security guarantees.
To help with this issue, Cosmos introduced something called Interchain Security. This allows appchains to borrow security help from a more established chain like the Cosmos Hub. By doing this, new appchains can get the security they need without having to gather a large number of validators right away. This makes it easier for new appchains to start and operate safely. While Interchain Security is a great solution, it also has some risks. It could lead to centralization if smaller validators drop out, leaving larger ones in control and making them attractive attack targets.
Summarizing what we have learned so far, general rollups are great in the security aspect but they fail to provide any kind of customization, whereas appchains provide customization but are limited in security. But what if we could combine the best of both deploying on a rollup, which means security right off the bat, while also benefiting from the customizability behind having their own dedicated environment?
This is exactly what application-specific rollups, or “RollApps”, are trying to accomplish. The idea essentially involves combining the aspect of security, scalability, and EVM-compatibility of general-purpose L2 rollups, with the flexibility and customizability of L1 appchains—creating a killer combination that puts more power than ever into the hands of Web3 developers.
But, it’s not that simple to build, deploy, and manage your own rollups. The technical expertise and resources needed, coupled with the constant efforts to maintain the rollup, makes it a tedious pursuit.
Enter RaaS — rollups-as-a-service that promises to abstract the development process of rollups and ease developers' lives.
Rollup-as-a-Service
RaaS — rollups-as-a-service — enters the scene with options to enable developers to deploy rollups for their apps swiftly and effectively. With RaaS providers, developers can easily deploy rollups without dealing with the complicated details of existing Appchain stacks. The RaaS ecosystem includes everything, from simple rollup tools to fully customizable one-click rollup setups.
Caldera is a one-click RaaS provider enabling anyone to launch an optimistic rollup.
Introducing Caldera
Caldera is a platform that allows anyone to launch high-performance, customizable, application-specific rollups with the Arbitrum Nitro and Optimism Bedrock frameworks.
Using Caldera, any project can efficiently launch its own rollup by leveraging dozens of integrations with leading infrastructure providers, ranging from Data Availability solutions to Account Abstraction providers. Additionally, Caldera offers built-in developer tools, such as the Bridge Interface and Block Explorer, along with chain-level customizations like Custom Native Tokens, and the rollup networks launched using Caldera are referred to as "Caldera Chains."
Rollup stacks
Currently, Caldera supports two different kinds of rollup stacks for development. These are-
Arbitrum Nitro
Arbitrum Nitro, a proven Optimistic rollup stack, powers both the flagship Arbitrum chain, known as Arbitrum One and Arbitrum Nova, a lower-cost chain designed for gaming. It currently secures over $6 billion in Total Value Locked (TVL) across its production chains.
Advantages of using Arbitrum Nitro
Transactions are 10-100x cheaper than Ethereum.
Provides faster block times, as fast as 250ms when under high throughput.
Ethereum equivalence, with full support for Ethereum smart contracts and developer tooling.
Arbitrum Nitro supports further cost reduction via Arbitrum Anytrust or Celestia DA.
Arbitrum Nitro offers the choice to support WASM smart contracts through Stylus and lets you pick your rollup's own native token.
Optimism Bedrock
Caldera enables the deployment of dedicated rollups using the OP stack (Optimism Bedrock). The OP stack is a battle-tested Optimistic Rollup stack, powering Optimism Mainnet and Base, Coinbase’s recently launched L2. Collectively, the OP stack secures over $3.5 Billion in TVL.
Advantages of using Optimism Bedrock
Provides cheaper transactions.
Faster block times with full support for Ethereum smart contracts and developer tooling.
Ability to opt into the Superchain, Optimism’s future network of chains that share bridging, governance, and interoperability.
Customizations
1. Native gas token
Using Caldera, developers enjoy the flexibility to choose any ERC20 token as the native token for their rollup, whether it's their own protocol token or stablecoins like USDC or DAI. This helps enhance user experience by potentially simplifying gas fees for users, making the overall process smoother and more user-friendly.
2. Alternative Data Availability
Caldera supports Alternative Data Availability (Alt-DA) by integrating with Celestia, Near, and Arbitrum Anytrust. To ensure that invalid transactions on a rollup can be identified and reversed, users need a method to confirm that the block data of the rollup is actually shared. Currently, most Ethereum rollups address this by uploading all rollup blocks to Ethereum and relying on it for data availability.
However, traditional Ethereum data availability can result in high and unpredictable costs because rollups must compete for limited space with other dApps and users on Ethereum. Consequently, more than 95% of the cost of a rollup transaction today is due to uploading data to Ethereum. Alternative data availability systems use innovative methods to separate data availability from a chain's settlement, significantly reducing costs and increasing throughput, which enhances the long-term scalability of rollups.
3. Decentralized Sequencing
Caldera uses Decentralized Sequencing via an integration with Espresso, a leading decentralized sequencing network. In a rollup, a sequencer organizes and verifies transactions, typically these sequencers have been centralized, and controlled by one party or a group, and currently, many rollups like Arbitrum One and Optimism Mainnet, use centralized sequencers.
However, centralized sequencers have drawbacks:
They create a single point of failure. If the sequencer fails, it can be hard or costly to add transactions.
They can censor or delay transactions, or reorder them to profit unfairly.
Users can't see how transactions are ordered.
Currently, users need to trust rollup operators to manage the sequencer properly, which isn't ideal. The Espresso Sequencer network changes this. It replaces the rollup's mempool with Espresso's sequencer. This means user transactions go to Espresso's sequencer instead of the rollup node. Rollup nodes then get sequenced transactions from Espresso, removing the need for a centralized sequencer and ensuring fair treatment.
Integrations and Partnerships
Caldera allows platforms to customize their rollup by partnering with various service providers. Such as-
1. LayerZero
Platforms using Caldera can benefit from LayerZero’s cross-chain communication protocol that supports direct, trustless communication across multiple blockchain networks.
2. Alchemy
Using Alchemy developers can boost their productivity with a range of essential APIs, SDKs, and tools for building and expanding applications.
3. Espresso
Espresso offers rollups deployed using Caldera and assures credible neutrality, enhanced interoperability, & long-term alignment with Ethereum.
4. Biconomy
Biconomy enables account abstraction, ensuring smooth onboarding and seamless user experience. It helps platforms using Caldera to scale by boosting user adoption and retention.
5. Celestia
Celestia is the first modular data availability (DA) network that allows platforms to scale with the number of users on their network.
Ecosystem and Use Cases
Caldera helps businesses of all sizes and types to set up efficient rollups, improve user experience, and enhance their on-chain operations. Some notable users of Caldera are-
1. Manta Network
Manta Network is the multi-modular ecosystem for ZK applications. One of its products, Manta Pacific, is an L2 network built by Caldera. It utilizes Celestia for its data availability layer.
2. Curio
Curio is a studio producing fully on-chain games. On-chain games tend to consume a lot of gas fees and require low latency. Caldera’s rollup infrastructure makes it possible for a gaming studio like Curio to put an entire game engine on-chain. Curio’s custom-built Caldera chain can easily handle 300 million gas per second, providing the power needed for a full on-chain gaming experience. What Ethereum would normally take 2 minutes to process, Curio’s Caldera chain can process in one second.
3. Injective Labs
Injective is a lightning-fast, interoperable, layer one blockchain optimized for building premier Web3 financial applications. Recently, Injective introduced inEVM, the first Ethereum Virtual Machine capable of achieving true composability across Cosmos and Solana which was made possible using Caldera's rollup infrastructure platform.
4. RARI Chain
Built with Caldera, RARI Chain is an EVM equivalent blockchain powered by Arbitrum Orbit that offers low costs, fast transactions, and a unique royalty system for NFT creators. With this deployment, NFT creators will finally have access to a performant infrastructure layer that prioritizes creator compensation by bringing royalties into the foundation of every project launched on the platform.
5. Hook
Hook is an NFT call options protocol that allows users to trade on NFT price movements. Using Caldera’s rollup infrastructure Hook has successfully reduced latency and cost while increasing throughput and enhancing the user experience.
Conclusion
Appchains are gaining popularity. As they grow, so does the reliance on rollups, which boost performance without raising costs. This makes services like Caldera even more important, as they simplify rollup deployment. In the future, RaaS providers will integrate with various tech stacks and expand their offerings and there is no doubt that RaaS will be a key component in the web3 developer stack.
Ready to deploy your first customized rollup? Head over to caldera.xyz